1. LinkedList 에 특징을 알아 보자
2. LinkedList 구현해 보기

자기 참조 관계
- 자기 참조는 객체가 자신과 같은 타입의 다른 객체를 가리키는 경우를 말한다.
- 용도 -> 연결 리스트, 트리 구조에 많이 활용
LinkedList 특징
- 동일한 데이터 타입을 순서에 따라 관리하는 자료 구조
- 자료를 저장하는 노드에는 자료와 다음 요소를 가리키는 링크(포인터)가 있음
- 자료가 추가 될때 노드 만큼의 메모리를 할당 받고 이전 노드의 링크로 연결함 (정해진 크기가 없음)
- jdk 클래스 : LinkedList
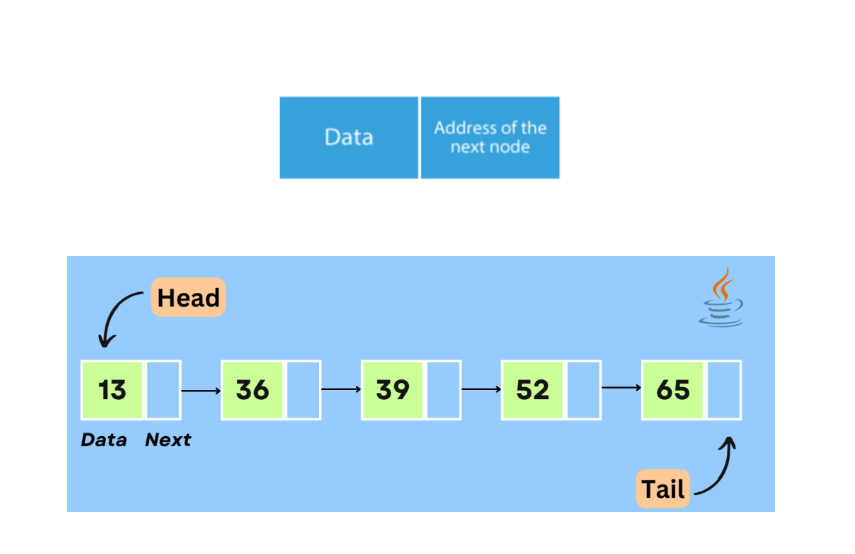
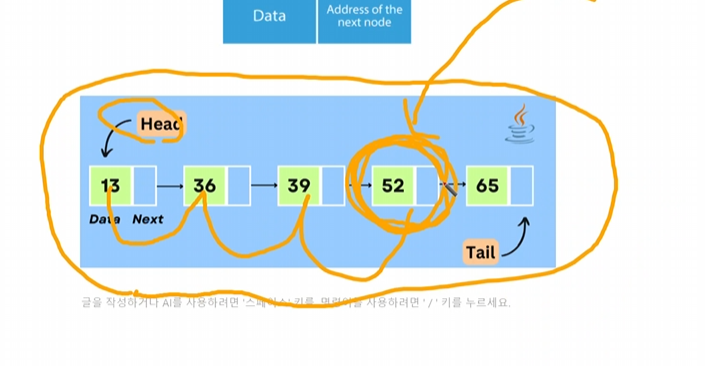
52라는 데이터를 찾으려면 Head에서부터 차례차례로 찾는다 -> next
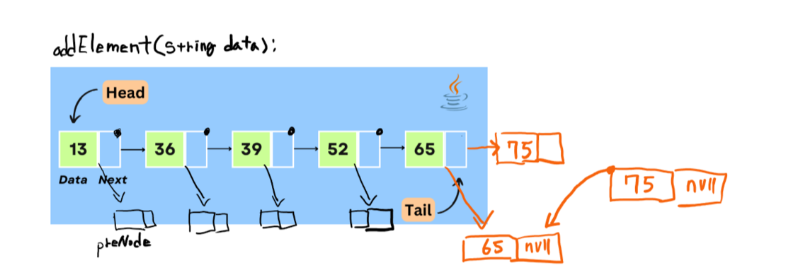
: 하나의 요소를 저장하는 기능 설계
package structure.ch04;
public class MyLinkedList {
private Node head; // 요소의 맨 처음을 가리킴
private int count; // 링크드리스트에 몇개의 요소가 연결 되어 있는 개수
// MyLinkedList 맨 처음 생성시 노드는 없는 상태
public MyLinkedList() {
head = null;
count = 0;
}
// 저장된 Node 갯수를 반환하는 메서드
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
// 새로운 노드(Node)를 1개 추가 하는 메서드를 만들자.
public Node addElement(String data) {
Node createNode = new Node(data);
if(head == null) {
// 맨 처음 요소를 저장하는 동작
head = createNode;
} else {
// 항상 요소 찾기는 head 부터 시작
Node preNode = head; // [야스오][](next)
// [야스오][] ---> [티모][] --> [소라카][]
while(preNode.next != null) {
preNode = preNode.next;
}
// 핵심 코드
//[티모][next] --> [next] = [소라카][]
preNode.next = createNode;
}
count++;
return createNode; // 추후 수정
}
// 테스트 코드
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList linkedList = new MyLinkedList();
linkedList.addElement("야스오");
linkedList.addElement("티모");
linkedList.addElement("소라카");
// [야스오][] ---> [티모][] ----> [소라카][]
System.out.println(linkedList.getCount());
} // end of main
} // end of class
특정 위치에 요소 삭제 하기
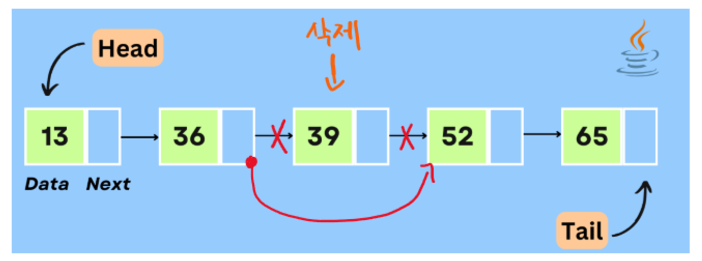
: 삭제 기능, 전체 출력 기능 추가
package structure.ch04;
public class MyLinkedList {
private Node head; // 요소의 맨 처음을 가리킴
private int count; // 링크드리스트에 몇개의 요소가 연결 되어 있는 개수
// MyLinkedList 맨 처음 생성시 노드는 없는 상태
public MyLinkedList() {
head = null;
count = 0;
}
// 저장된 Node 갯수를 반환하는 메서드
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
// 새로운 노드(Node)를 1개 추가 하는 메서드를 만들자.
public Node addElement(String data) {
Node createNode = new Node(data);
if(head == null) {
// 맨 처음 요소를 저장하는 동작
head = createNode;
} else {
// 항상 요소 찾기는 head 부터 시작
Node preNode = head; // [야스오][](next)
// [야스오][] ---> [티모][] --> [소라카][]
while(preNode.next != null) {
preNode = preNode.next;
}
// 핵심 코드
//[티모][next] --> [next] = [소라카][]
preNode.next = createNode;
}
count++;
return createNode; // 추후 수정
}
public Node removeElement(int index) {
// 방어적 코드
// 0 , 1
if(index >= count) {
System.out.println("삭제할 위치 오류. 현재 리스트 개수는 " + count + " 입니다");
return null;
}
// 맨 앞 요소를 삭제 요청 시
// 항상 요소를 찾을 때 시작은 head 부터 시작이다.
Node tempNode = head;
if(index == 0) {
// 코드 시작전 모습
// [야스오][티모.주소값] --> [티모][null]
head = tempNode.next;
// 코드 수행 후 모습
// [티모][null]
} else {
// 코드 시작전 모습 : postion -> 2 라고 가정 --> n - 1 ---> [1]
// [야스오][티모.주소값] --> [티모][소라카.주소값] --> [소라카][null]
Node preNode = null;
for(int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
preNode = tempNode;
tempNode = tempNode.next;
}
preNode.next = tempNode.next;
} // end of if
count--;
// System.out.println(positon + " 번째 요소를 삭제 했습니다.");
return tempNode; // todo - 추후 수정
}
// 전체 출력 하는 기능 만들기
public void printAll() {
if(count == 0) {
System.out.println("출력할 내용이 없습니다");
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while(temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.getData());
temp = temp.next;
if(temp != null) {
System.out.print("-->");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
// 테스트 코드
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList linkedList = new MyLinkedList();
linkedList.addElement("야스오");
linkedList.addElement("티모");
linkedList.addElement("소라카");
linkedList.addElement("애쉬");
linkedList.addElement("가렌");
linkedList.printAll();
linkedList.removeElement(4);
linkedList.printAll();
// [야스오][] ---> [티모][] ----> [소라카][]
//System.out.println(linkedList.getCount());
} // end of main
} // end of class실행 결과_____
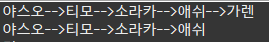
: 하나의 요소 출력, 전체 삭제 기능 추가
package structure.ch04;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class MyLinkedList {
private Node head; // 요소의 맨 처음을 가리킴
private int count; // 링크드리스트에 몇개의 요소가 연결 되어 있는 개수
// MyLinkedList 맨 처음 생성시 노드는 없는 상태
public MyLinkedList() {
head = null;
count = 0;
}
// 저장된 Node 갯수를 반환하는 메서드
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
// 새로운 노드(Node)를 1개 추가 하는 메서드를 만들자.
public Node addElement(String data) {
Node createNode = new Node(data);
if(head == null) {
// 맨 처음 요소를 저장하는 동작
head = createNode;
} else {
// 항상 요소 찾기는 head 부터 시작
Node preNode = head; // [야스오][](next)
// [야스오][] ---> [티모][] --> [소라카][]
while(preNode.next != null) {
preNode = preNode.next;
}
// 핵심 코드
//[티모][next] --> [next] = [소라카][]
preNode.next = createNode;
}
count++;
return createNode; // 추후 수정
}
public Node removeElement(int index) {
// 방어적 코드
// 0 , 1
if(index >= count) {
System.out.println("삭제할 위치 오류. 현재 리스트 개수는 " + count + " 입니다");
return null;
}
// 맨 앞 요소를 삭제 요청 시
// 항상 요소를 찾을 때 시작은 head 부터 시작이다.
Node tempNode = head;
if(index == 0) {
// 코드 시작전 모습
// [야스오][티모.주소값] --> [티모][null]
head = tempNode.next;
// 코드 수행 후 모습
// [티모][null]
} else {
// 코드 시작전 모습 : postion -> 2 라고 가정 --> n - 1 ---> [1]
// [야스오][티모.주소값] --> [티모][소라카.주소값] --> [소라카][null]
Node preNode = null;
for(int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
preNode = tempNode;
tempNode = tempNode.next;
}
preNode.next = tempNode.next;
} // end of if
count--;
// System.out.println(positon + " 번째 요소를 삭제 했습니다.");
return tempNode; // todo - 추후 수정
}
// 전체 출력 하는 기능 만들기
public void printAll() {
if(count == 0) {
System.out.println("출력할 내용이 없습니다");
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while(temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.getData());
temp = temp.next;
if(temp != null) {
System.out.print("-->");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
// 지정한 위치의 노드 하나만 출력 하기
public Node getNodeByIndex(int index) {
if(index >= count) {
System.out.println("검색 위치 오류 - 잘못된 요청");
}
Node tempNode = head;
if(index == 0) {
return head;
}
// [야스오][티모.주소값] --> [티모][] --> [소라카][]
for(int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
tempNode = tempNode.next; // 다음 요소는 무조건 next 에 담겨 있다.
}
return tempNode;
}
// 전체 삭제 기능
public void removeAll() {
head = null;
count = 0;
}
// 테스트 코드
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList linkedList = new MyLinkedList();
linkedList.addElement("야스오");
linkedList.addElement("티모");
linkedList.addElement("소라카");
linkedList.addElement("애쉬");
linkedList.addElement("가렌");
linkedList.printAll();
linkedList.removeElement(4);
linkedList.printAll();
System.out.println(linkedList.getNodeByIndex(1).getData());
// [야스오][] ---> [티모][] ----> [소라카][]
//System.out.println(linkedList.getCount());
linkedList.removeAll();
linkedList.printAll();
} // end of main
} // end of class실행 결과______

public Node addElement(String data) {
Node createNode = new Node(data); // (data) 뺴먹음 -> data 안 적으면 null 값이 출력됨
if (head == null) {
// 맨 처음 요소를 저장하는 동작
head = createNode;
Node createNode = new Node(data) ◀ data 빼먹으면 data 값 출력이 안됨 null 값이 출력됨 !
'JAVA > Java 기초' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA] 프레임워크(collection framework) (0) | 2024.05.16 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA] 자바 I/O 개론 (0) | 2024.05.16 |
| [JAVA] 큐(Queue) (0) | 2024.05.07 |
| [JAVA]이미지 올리기 (0) | 2024.04.29 |
| [JAVA] 기초 - 함수와 메서드 (1) | 2024.04.19 |